Acne - symptoms and treatment
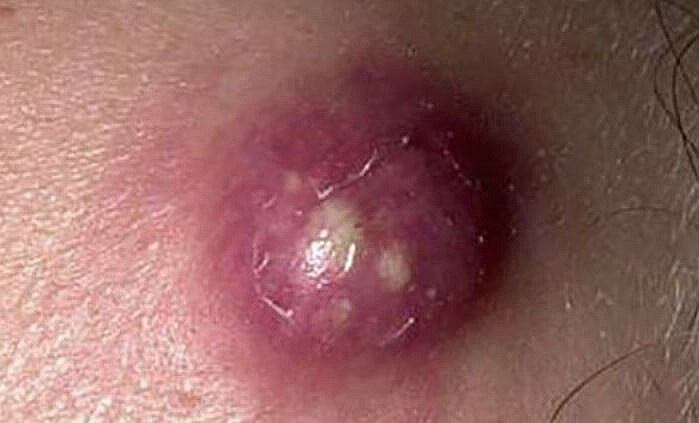
A furuncle (acne) is a purulent necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle and the connective tissue and fat around it. In everyday life, it is called chirium or abscess.
Furuncles develop because of infection: 95.4% of cases are caused by Staphylococcus aureus. In 4.6% of people, organisms other than this bacteria are present
In the early stages, a small, painful, reddish nodule forms around the hair follicle—an organism’s reaction to bacterial introduction. Over time, this tumor enlarges, becoming cone-shaped or pyramidal, towering over the skin. Pain becomes more intense, and purulent content appears around the hair.
furuncle usually occur on areas of thick hair, such as the mustache, beard, head, nape of the neck, forearms, hands, inner thighs, lumbar area, and buttocks. They do not develop in the mouth and on the palms or soles.
One cause of furuncles is folliculitis, an inflammation that affects only the hair follicle and is represented by a small yellowish bleb with a hair in the center. If squeezed, the infection may spread to nearby tissue, resulting in the formation of a boil. It can also occur when blackheads are pressed out.
Risk factors acne
- furuncle predispose to the development of:
- Skin contamination, such as when changing towels is not timely
- linen and bedding
- sparse hand washing
- razor sharing
- towels and sponges with other family members.
If the acne has already developed, wash the affected skin with soap or a low pH cleanser and change bed linen, clothing, and towels daily
Microinjuries due to rubbing of clothes or skin scratches, itchy dermatoses, cuts, and scratches
High humidity at high air temperature.
Hypothermia or overheating of the body
Immune and endocrine disorders include HIV infection and other immunodeficiency disorders, diabetes, hormonal imbalances, and obesity.
Chronic diseases such as atherosclerosis and heart failure
Nasal staphylococcus aureus carrier
In addition, environmental degradation, as well as the widespread, uncontrolled and often illiterate use of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory agents, upsets the balance in microbial communities and leads to the predominance of opportunistic microflora
What complications may occur
- Boils may spread to other parts of the body
- And there may be a blood infection.
What you can do acne
Wash hands with antibacterial soap before touching the furuncle and after touching the furuncle (regardless of the wound or purulent head).
Gently apply an antibacterial agent on the affected area three to four times a day. Apply a warm compress for 15 minutes three to four times a day to relieve pain and accelerate pustular head maturation. Then close the furuncle with a thick layer of gauze and keep the dressing dry. In no case do not scratch or pick the furuncle, do not squeeze and do not open the furuncle yourself, as this can spread infection. If the boil opens on its own, gently remove the pus, then carefully treat the area with hydrogen peroxide. Then apply a dry bandage. Repeat the procedures every day until they are fully healed. Take an anesthetic to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Do not use over-the-counter medications (creams, ointments) that contain antibiotics without consulting a doctor. Never attempt to open the furuncle yourself without a doctor's permission.
Wash hands thoroughly before cooking because bacteria from boils can contaminate food. Diabetics who develop boils should see a doctor immediately.
You need to apply the ointment to the acne or furuncle.