Tooth abscess
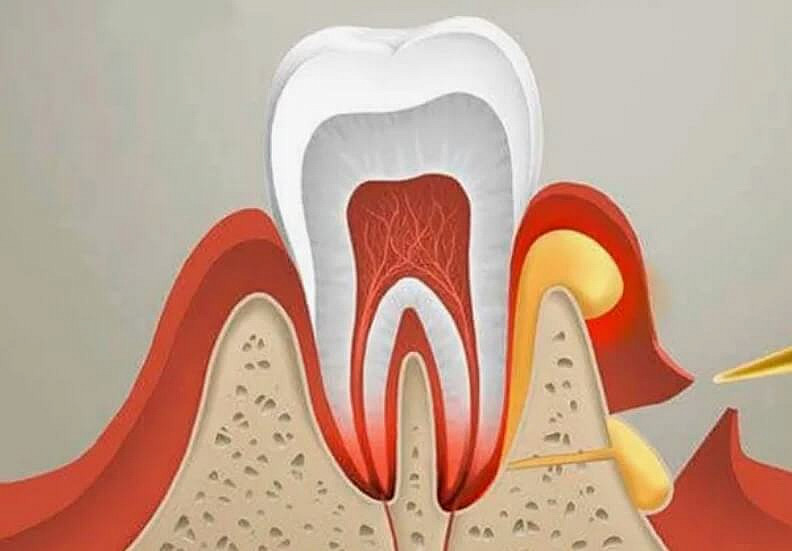
A tooth abscess, also known as a dental or dentioalveolar abscess, is a serious infectious disorder that occurs as a complication of dental caries. Then pus accumulates in the tissues surrounding the tooth, resulting in a cavity in the bone tissue. It is one of the most common odontogenic infections where "odontos" means "tooth" in Greek, emphasizing that the source of the problem is teeth. If the infection spreads, it may pose a threat not only to health, but also to the life of the patient.
Signs of Tooth Abscess
Tooth abscess causes a variety of symptoms. Acute, throbbing, and often spontaneous pain is the primary and most prominent sign. It occurs suddenly, especially in the evening or at night, and becomes stronger over time. The pain may radiate into the ear, angle of the jaw, or neck, becoming worse when biting on the affected side. The pain is very mild, and the patient cannot clearly identify which tooth is hurting - the discomfort extends to the entire side of the jaw.
- In addition to pain, other symptoms include
- unpleasant smell (putrid) and taste in the mouth;
- body temperature rise to 37.5-38 °C and above;
- signs of intoxication: headache, weakness and other manifestations;
- difficulty opening the mouth and swallowing
- sleep and appetite disorders
- mucosal redness and edema
- swelling of the soft tissues of the face, which can change its shape;
- Change the color of the affected tooth to gray.
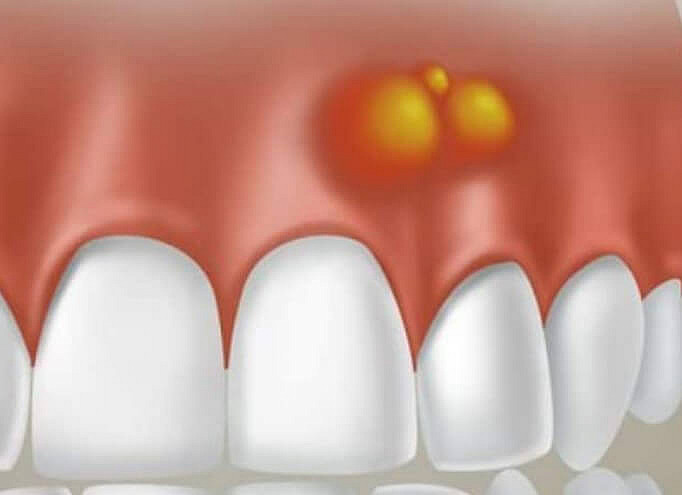
Factors of occurrence
Tooth abscess is most often caused by tooth decay and its complications. Therefore, the disorder is also called odontogenic infection. This process may take years before an abscess forms.
However, there are other factors that may contribute to the abscess:
Complications and consequences of dental procedures such as surgery.
Accidental infection due to anesthesia.
Ignoring the doctor's recommendations when treating periodontitis and other complications of caries.
Dental injuries.
- Complications after endodontic treatment, including broken instruments, perforated root wall, root fractures and other problems.
- Treatment
- Treatment of a dental abscess depends on the shape and condition of the abscess. In mild cases, treatment can be outpatient, in more complex cases, in the context of an inpatient oral and maxillofacial surgery. The main goal of treatment is to drain the pus and eliminate the focus of inflammation.
Conservative treatment of a periodontal abscess includes drainage of the purulent lesion. After that, curettage of the gingival pockets is carried out. Antibiotic therapy is the mainstay of treatment.
Unfortunately, the causative tooth cannot always be saved and must be removed before the affected tissue can be surgically cleaned and excised. If it recurs after surgery for a periodontal abscess, tooth extraction is recommended.
Regardless of the treatment chosen for a tooth abscess, antibiotic therapy is given to the focus of infection. First, broad-spectrum antibiotics are given, and once bacteria are sensitized to drugs, narrow-spectrum drugs are used.
Prophylaxis against tooth abscess
To prevent a tooth abscess, it is important to maintain good personal hygiene and treat dental problems in a timely manner. The main cause of abscess is odontogenic infection, so the following recommendations should be followed:
Regular visits to the dentist: it is necessary to undergo preventive examinations at least twice a year. Patients at risk may require more frequent visits to the dentist.
Oral hygiene: Brush your teeth twice a day using a brush, paste, flosses and irrigators. Despite all efforts, a toothbrush and paste cannot completely remove plaque. Therefore, it is recommended to perform a professional oral cleaning at the dentist every six months.
Diet adjustment: reduce consumption of sweets and sticky foods. Fresh vegetables, fruits and other foods that require careful chewing should be preferred.
Following these recommendations can help reduce the risk of tooth abscess and maintain good oral health.

